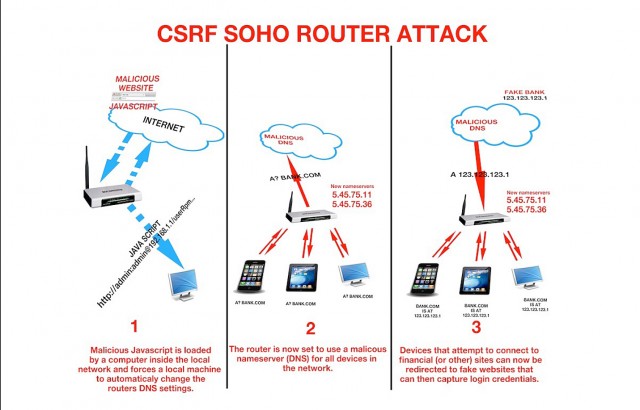
Researchers said they have uncovered yet another mass compromise of home and small-office wireless routers, this one being used to make malicious configuration changes to more than 300,000 devices made by D-Link, Micronet, Tenda, TP-Link, and others.
The hackers appear to be using a variety of techniques to commandeer the devices and make changes to the domain name system (DNS) servers used to translate human-friendly domain names into the IP addresses computers use to locate their Web servers, according to a report published Monday by researchers from security firm Team Cymru. Likely hacks include a recently disclosed cross-site request forgery (CSRF) that allows attackers to inject a blank password into the Web interface of TP-Link routers. Other attack techniques may include one that allows wireless WPA/WPA2 passwords and other settings to be remotely changed.
So far, the attacks have hijacked more than 300,000 servers in a wide range of countries, including Vietnam, India, Italy, Thailand, and Colombia. Each compromise has the potential to redirect virtually all connected end users to malicious websites that attempt to steal banking passwords or push booby-trapped software, the Team Cymru researchers warned. The campaign comes weeks after researchers from several unrelated organizations uncovered separate ongoing mass hacks of other routers, including a worm that hit thousands of Linksys routers and the exploit of a critical flaw in Asus routers that exposes the contents of hard drives connected by USB.
Read 7 remaining paragraphs | Comments